Bitcoin Staking
Bitcoin staking in Babylon protocol enables BTC holders to lock their assets in a time-bound contract as security collateral, earning rewards for securing networks. The protocol implements a slashing mechanism where staked assets may be forfeited if protocol security rules are violated, similar to traditional security deposits but with protocol-enforced penalties.
Native Bitcoin Staking Implementation
Babylon's staking mechanism is built directly on Bitcoin's UTXO model and native scripting capabilities. This differs from traditional cross-chain staking solutions that require wrapping or bridging Bitcoin to external networks.
Core Requirements
For protocol security, Bitcoin staking implements the following attributes:
- Self-custody: Stakers maintain direct control of their Bitcoin
- Trustless execution: No reliance on third parties
- Native operation: Direct integration with Bitcoin blockchain
- Slashing capability: Protocol-enforced penalties for malicious behavior
Technical Implementation
The staking mechanism leverages Bitcoin's UTXO model, allowing holders to create multiple UTXOs with distinct spending conditions defined through Bitcoin scripts. These scripts form the basis of staking contracts with the following conditions:
- Holder's cryptographic signature
- Time-lock expiration
- Covenant committee consensus (for slashing)
The protocol introduces Extractable One-Time Signatures (EOTS) and a covenant committee to enable slashing functionality. The committee can execute slashing through majority consensus if malicious behavior is detected, resulting in partial or complete forfeiture of staked assets.
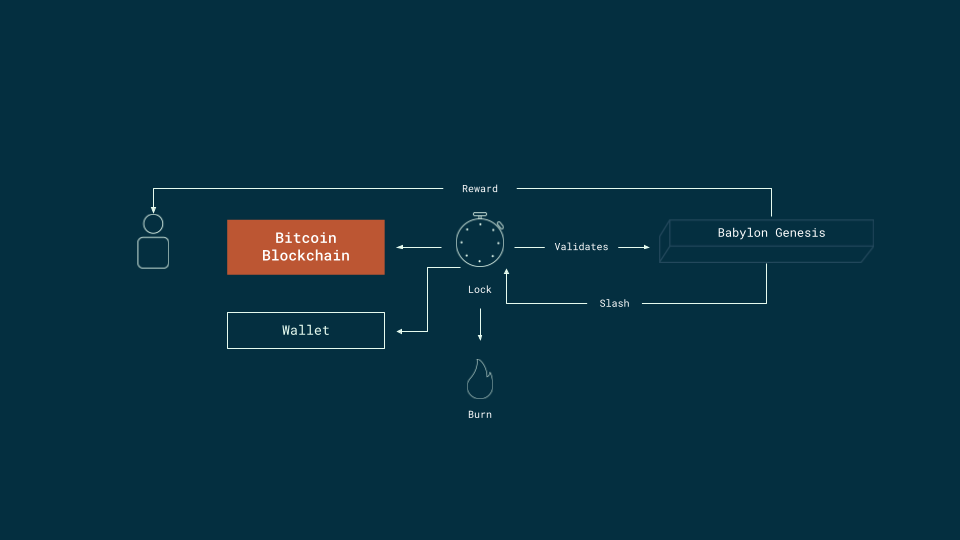
The Babylon Staking Protocol maintains an index of staked Bitcoin by monitoring and validating transactions between Bitcoin Chain and Babylon Genesis.
Staking Architecture
Bitcoin Staking enables BTC holders to delegate their assets to Finality Providers. This architecture forms the foundation of Babylon's security model, allowing stakers to participate in securing the network while earning rewards.
Protocol Components
The staking architecture consists of:
- Staking Contract: Bitcoin script-based security mechanism with covenant committee integration, facilitated via Babylon Genesis
- Finality Provider: Delegated validators for chain or data validation
- Babylon Genesis: Coordination layer that tracks staking state and distributes rewards
Security Properties
The security model provides:
- Slashable PoS Security: Guaranteed partial stake forfeiture upon safety violations
- Asset Safety: Guaranteed withdrawal capability for honest stakers and validators
- Liquidity Assurance: Secure, efficient unbonding without social consensus requirements
Protocol Benefits
This architecture optimizes Bitcoin's utility as security collateral without requiring additional capital allocation. It addresses the cold-start problem faced by new blockchain networks in bootstrapping security capital and trust. The slashing mechanism creates strong security incentives, as malicious behavior results in stake loss.